축하합니다.
우리 연구실 Zahra Nourmohammadi, 유예지 학생이 2021 춘계 ITS학술대회에서 “해양사고 예측을 위한 머신러닝 기법 적용방안 연구” 라는 주제로 우수논문상을 수상하였습니다.
모두 수고했습니다.!!

축하합니다.
우리 연구실 Zahra Nourmohammadi, 유예지 학생이 2021 춘계 ITS학술대회에서 “해양사고 예측을 위한 머신러닝 기법 적용방안 연구” 라는 주제로 우수논문상을 수상하였습니다.
모두 수고했습니다.!!

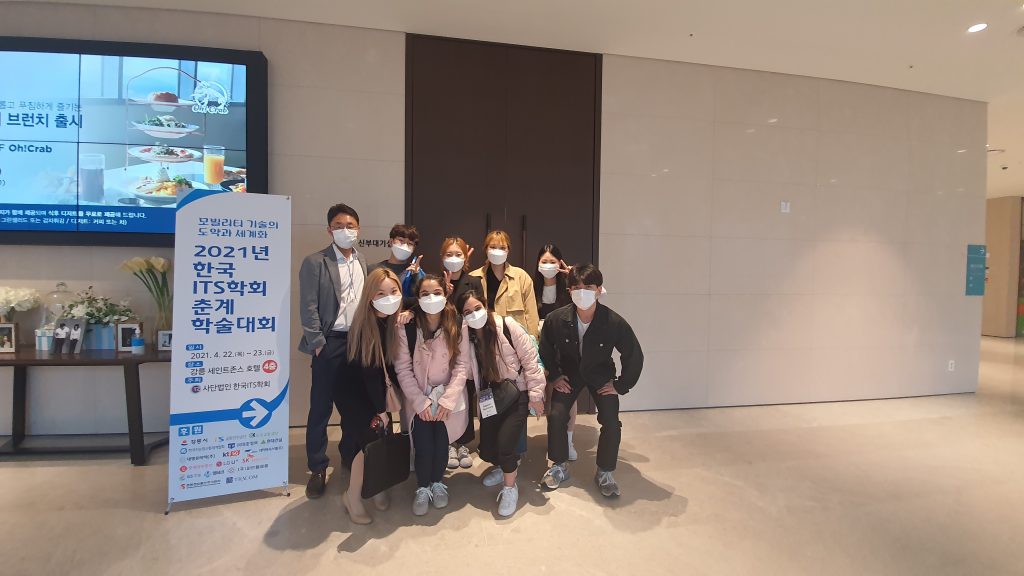
2021 춘계 ITS 학회가 2021년 4월 22~23일 강릉에서 개최되었습니다.





Title: Personalized autonomous driving maneuver based on reinforcement learning
Abstract:
It is evident that road users will be changed from human-driven cars to automated-driven cars in the future by progressive research trends. However, the adoption of autonomous vehicles in our daily life is controversial in many different aspects since people have not ready to accept autonomous vehicles yet. Significant concerns are safety and reliability. According to Reuters[1], 67 percent of respondents considered that the safety standard of autonomous vehicle driving should be higher than conventional vehicle driving. Plus, on 2020 March, almost half of the Americans responded that they would never take autonomously driven cars, and 60% of respondents said they would have more trust in the auto-driven car if they understand how it works[2]. People tend to think that ten more years is required to believe automated driving system[2].
In order to answer the questions above, car manufacture such as Tesla, Hyundai, and so on have been putting so much effort to bring the autonomous vehicle era to us sooner [3, 4]. However, autonomous technology is still insufficient for being used in reality yet. The manufactures offer only driving assistance systems so far, such as the Advanced Driver Assistance System(ADAS), and recommend people to use the systems only on the highway. The primary reason for driving automatically in the urban area is complicated because of the lack of infrastructure for communication and plenty of components to consider for safe driving compared to highway[5-8].
When it comes to urban areas, the typical types of intersections can be categorized into a signalized and unsignalized intersections. In the case of the signalized intersection, traffic signal plays a role in maximizing the traffic flow efficiency under the premise of ensuring crossing priority. However, unsignalized intersection is a totally different story. Although fewer cars might cross the intersection than signalized one, the priority of crossing the intersection has to rely on each driver’s decision making since most countries outside of North America, and South Africa does not adjust stop sign rule[9]. Therefore, traffic at unsignalized intersections not only considers crossing the intersection safely but also needs to be react similarly to how humans drive. Many researchers have begun to focus on the study on unsignalized intersection control to give people trustworthy autonomous driving experience. Therefore, people would trust and ride autonomous vehicles in the future. In this study, the techniques that consider the human experience and make a car drive autonomously will be investigated.
When it comes to consider the human experience, human-in-the-loop(HITL) and Virtual Reality(VR) technology are implemented for this study. The HITL approach gets the spotlight due to the inability of a computer system to accurately accomplish tasks, which require human participation [10-12]. VR technology is prevalently used to offer a realistic experience to participants [13]. By integrating two techniques, it has the potential to carry out practical driving behavior datasets involving human experience.
In the case of getting an autonomously driven maneuver supervised(ref) and reinforcement learning(ref) have already been conducted. Among them, reinforcement learning(RL) has been paying attention due to its feature that the agent is able to do self-study cooperating with the environment. The remarkable benefit of reinforcement learning is that it could give a better solution that the human being even never thought about or show technique that very limited people could perform. In addition, in a computer science field, they have started considering putting human experience or human knowledge in the middle of the reinforcement learning procedure to find the optimized result quickly[14]. Likewise, the agent considering individual’s preference by human-in-the-loop technique has been used in a different area. For example, the fashion industry developed a personalized outfit recommendation system depending on each customer’s taste, StyleSnap service from Amazon. Therefore, it would be worthy of researching optimized autonomous driving maneuvor based on individual’s driving habit. The research gaps that can be filled are as follows:
김인희 교수가 과학기술정보통신부가 주관하고 한국연구재단이 지원하는 2021년도 기초연구사업 신진연구자 지원 사업에 선정됐다.
한국연구재단 기초연구사업의 신진연구자 지원 사업은 연구자의 창의적 연구의욕 고취 및 연구역량 극대화를 통해 우수 인력을 양성하고 국가 경쟁력을 제고하기 위한 사업으로, 김인희 교수는 5년간 약 7억원의 연구비를 지원 받게 된다.
과제명: Covid-19 시대의 공유 모빌리티와 대중교통을 연계한 교통운영 방안
축하합니다.
권동현, 박솔은 학생이 2020 한국 ITS학회 추계 학술대회에서 우수논문상을 수상하였습니다!!

□ 일정/장소
○ 일정: 2020년 11월 19일(목) ~ 20일(금)
○ 장소: 제주한라대학교 한라컨벤션센터
□ 학술대회 주제
○ 그린뉴딜정책에 따른 ITS의 확대 추진 및 고도화
□ 논문 제목





TOMMs와 TUPA의 합작으로 특허 출원!!

TUPA 3학년 정재은 “GPS TRAJECTORY DATA기반 통행비용함수 보정방안” 주제로 2020 교통학회 논문 발표하여 우수 논문상 수상



© 2026 TUPA. All rights reserved.