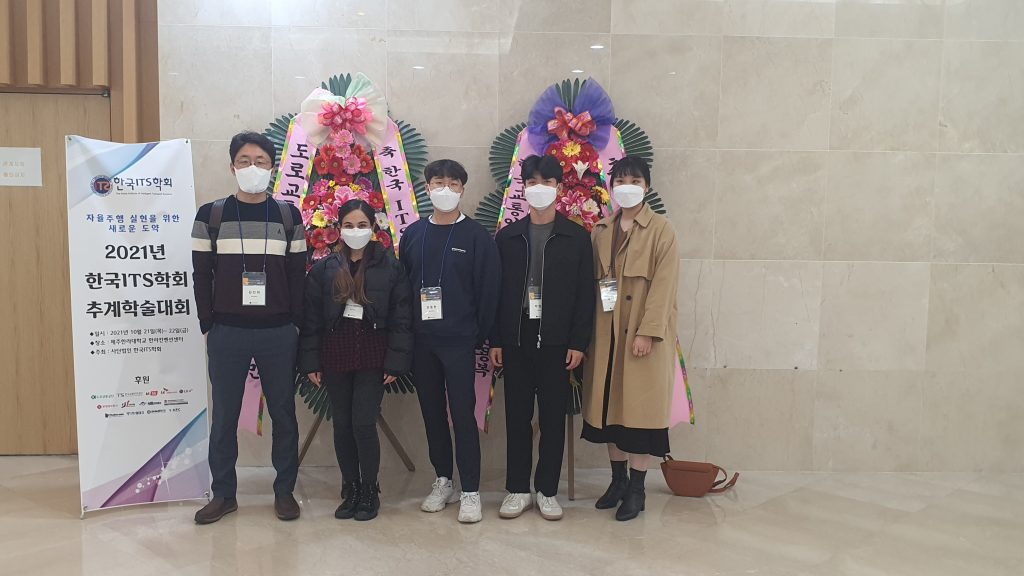
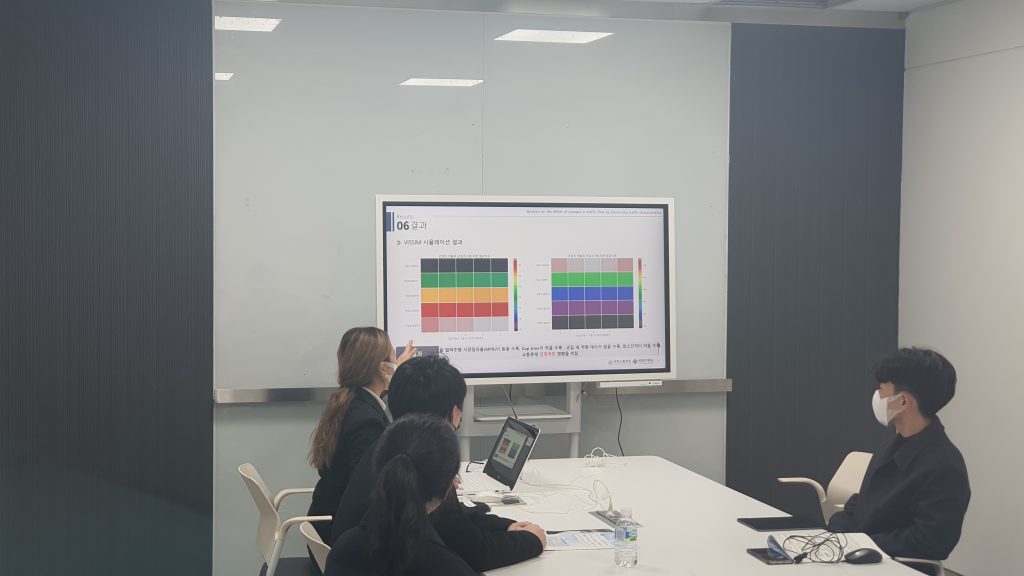
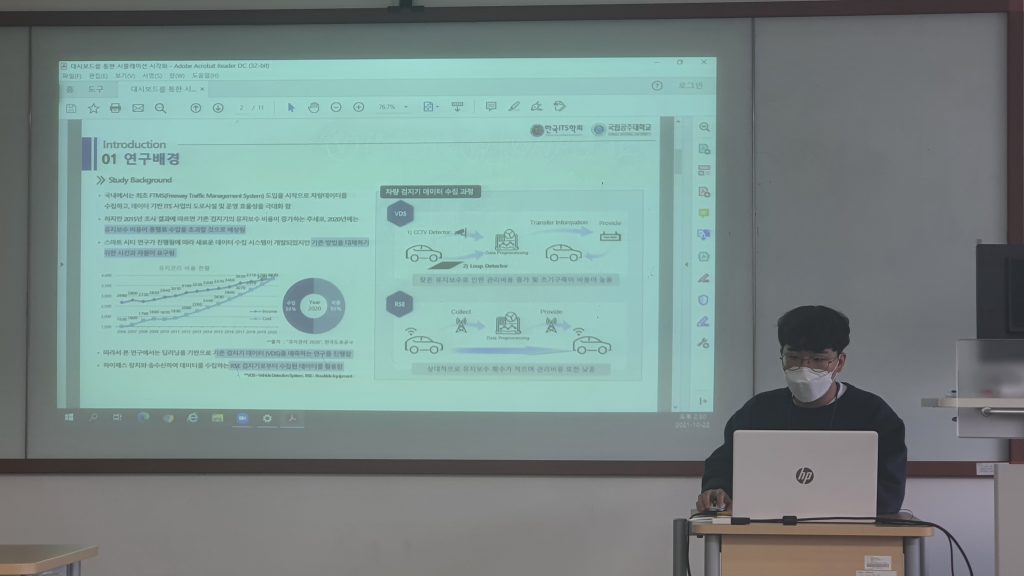
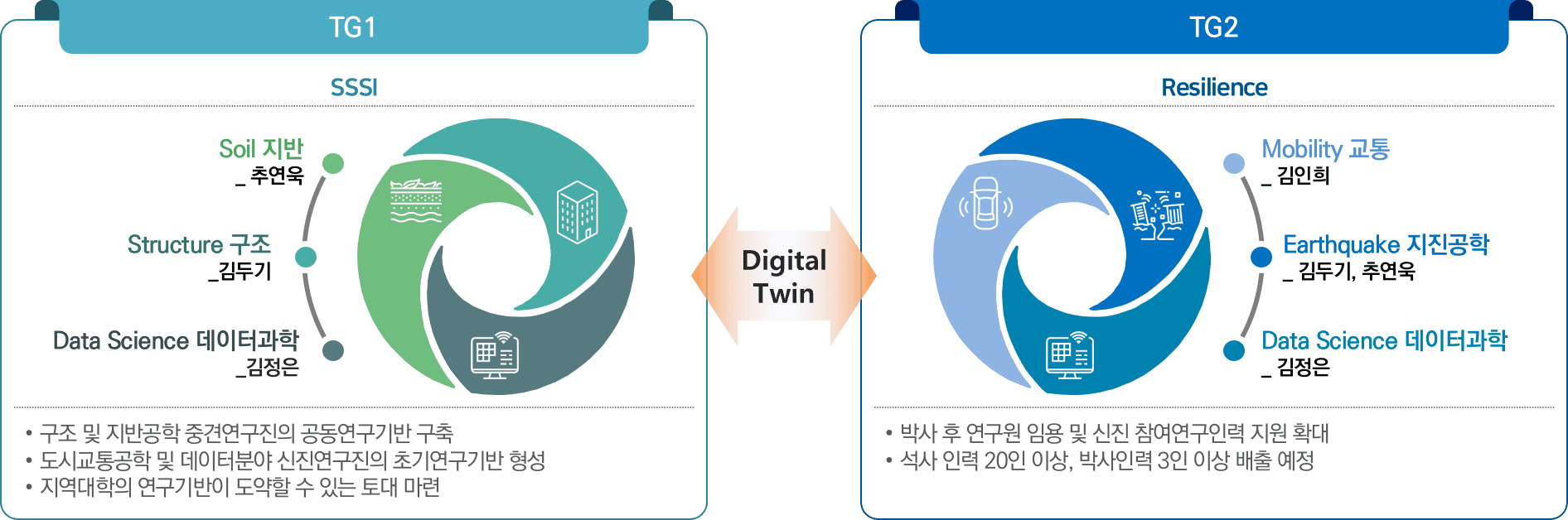
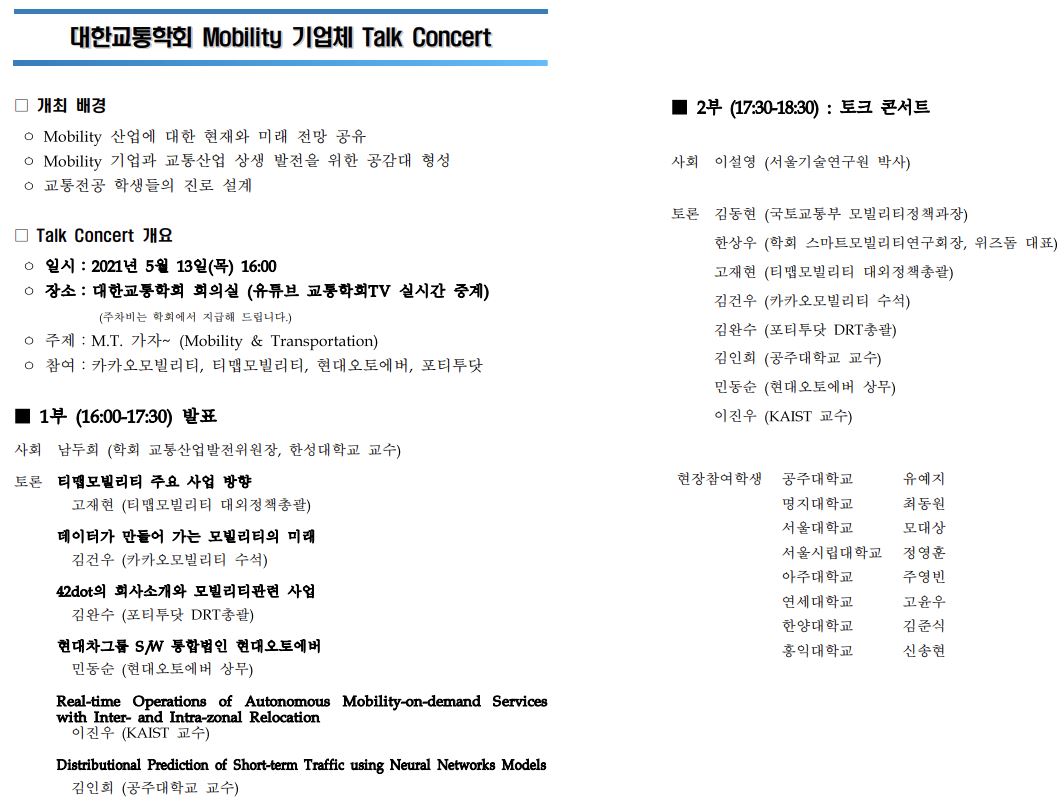
Tupa 가 제주도에서 11월 10일부터 11일까지 열린 제 85회 추계 교통학술대회에서 편의 논문을 발표하였습니다.
- 오픈소스를 이용한 교통데이터 시각화 by 정재은
- 보행자 편의성 향상을 위한 메타버스 기술 활용방안 by 박현철
- 군집주행의 비율과 군집주행내 차량 대수가 교통류에 미치는 영향 분석 by 유예지
- Ocean Accident Prediction based on Deep Learning Model in Blackspots found by Clustering Algorithms in Territorial Sea of South Korea by Zahra
- Vessel Trajectory Big data analysis using Apache Spark and prediction based on Machine Learning by Fatemeh
- 그래프 딥러닝 모델 기반 RSE검지기 교통량 데이터 예측연구 by 권동현
- Mircosimulation 통합 VR Multi-Agent Driving Simulator Platform 개발연구 by 오태호